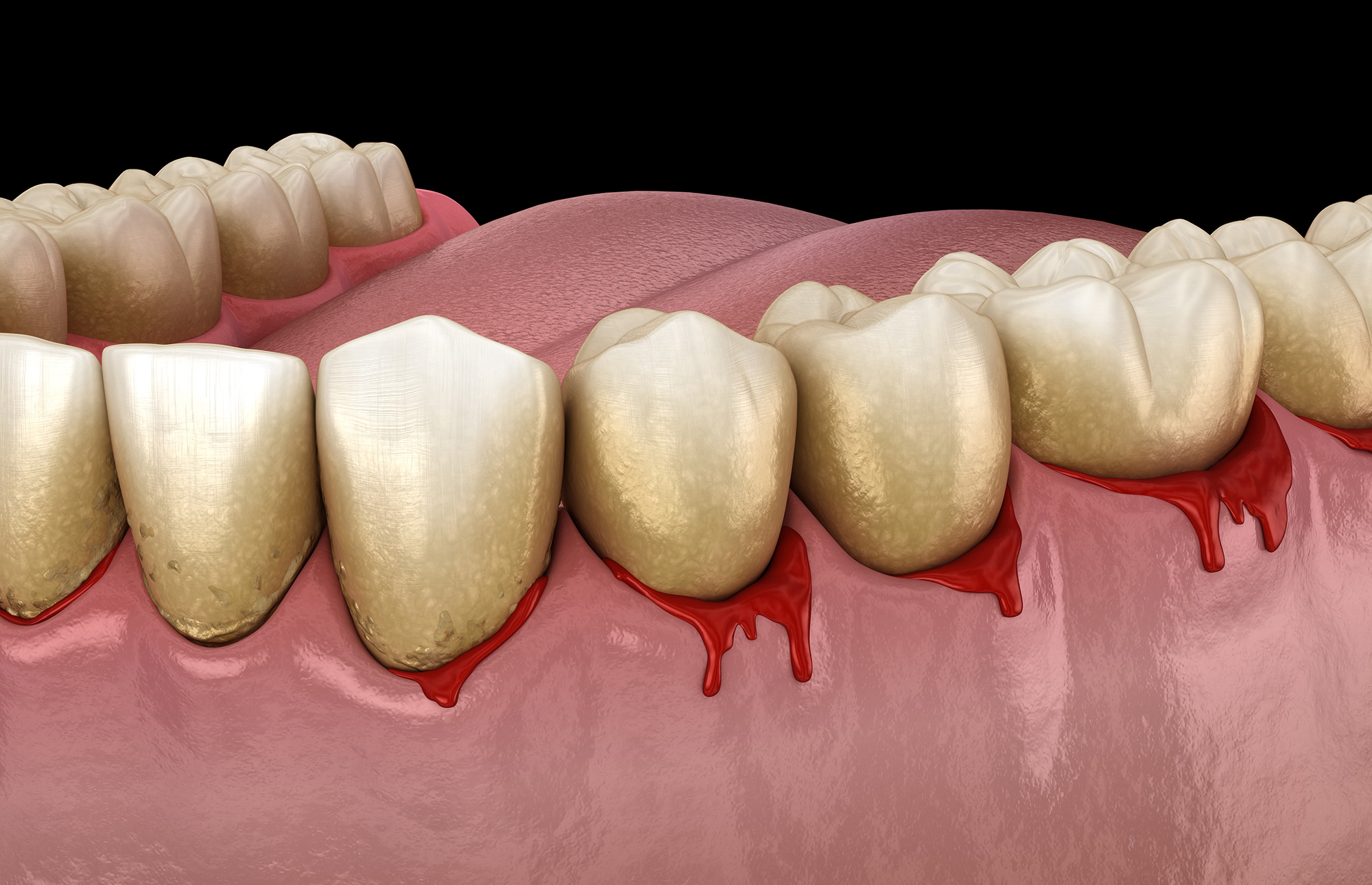
Bleeding gums are more than just a minor inconvenience; they are a window into your overall health and a potential warning sign of underlying issues that should not be ignored. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the myriad reasons why gums may bleed, backed by the latest scientific research. From everyday habits to systemic health conditions, understanding the causes of gum bleeding is the first step towards prevention and optimal oral health.
The Multifaceted Causes of Bleeding Gums
Gum bleeding is a symptom, not a disease in itself, and it can stem from a variety of causes. Each of these factors contributes to the condition in different ways, and understanding them is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Gingivitis to Periodontitis
Medication Side Effects
Certain medications, including blood thinners, can increase the likelihood of bleeding gums. These medications decrease the blood's ability to clot, which can lead to easier bleeding, even from mild irritations such as brushing or flossing.
Underlying Health Conditions
Prevention and Treatment: The Road to Healthier Gums
Preventing and treating bleeding gums is essential for maintaining not just oral health, but overall well-being. The following strategies can significantly reduce the risk of gum bleeding:
Adopting a Rigorous Oral Hygiene Routine
Regular Dental Check-ups
Managing Medications
Controlling Underlying Conditions
Bleeding gums are a sign that your body is fighting against infection, inflammation, or the effects of certain medications. By understanding the underlying causes and implementing preventive measures, you can protect your gums and your health. Remember, healthy gums are the foundation of a healthy body, and taking care of your oral health is an investment in your overall well-being.
Don't let bleeding gums go unchecked. Embrace the journey towards a healthier mouth and body today.